2P_sr.py¶
Description¶
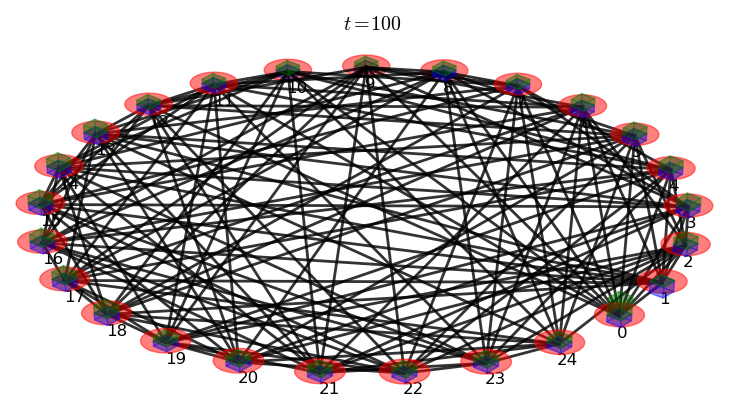
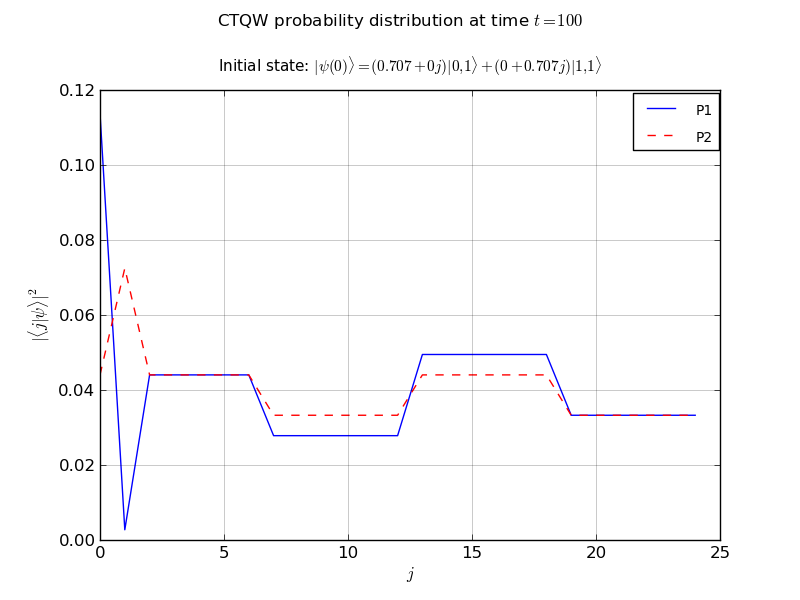
This example propagates a 2 particle continuous-time quantum walk on the first member of the strongly regular \((25,12,5,6)\) family of graphs.
- Amongst the features used, it illustrates:
the use of the Krylov propagation algorithm
- various plotting abilities:
- probability vs node plot
- probability and graph plot
Required Files¶
Source Code¶
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 | #!/usr/bin/env python2.7
# initialize PETSc
import sys, petsc4py
petsc4py.init(sys.argv)
from petsc4py import PETSc
import numpy as np
# import pyCTQW as qw
import pyCTQW.MPI as qw
# get the MPI rank
rank = PETSc.Comm.Get_rank(PETSc.COMM_WORLD)
if rank == 0:
print '2P Strong Regular CTQW'
# initialise a 25 node 2P graph CTQW,
# and create a Hamiltonian from a file.
walk = qw.Graph2P(25)
walk.createH('../graphs/strong-regular-25-12-5-6/1.txt','txt',layout='circle')
# create the initial state (1/sqrt(2)) (|0,1>+i|1,1>)
init_state = [[0,1,1.0/np.sqrt(2.0)], [1,1,1.0j/np.sqrt(2.0)]]
walk.createInitState(init_state)
# Propagate the CTQW using Krylov subspace methods
walk.propagate(100,method='krylov')
# plot the p1 and p2 marginal probabilities
# after propagation over all nodes
walk.plot('out/2p_sr_plot.png')
# plot a 3D graph representation with bars
# representing p1 and p2 marginal probabilities
walk.plotGraph(output='out/2p_sr_graph.png')
# destroy the quantum walk
walk.destroy()
|